To map the Universe is an unbelievably hard task. The sheer distance between the stars that we see in the night sky is incomprehensible for the human minds that favourably gaze upon them. The light that is born as a result of tumultuous churning of atoms in the heart of a star crosses light-years to reach our eyes.
The scale of things involved in this process is simply mind-boggling. However, whatever we see is just a small slice of a much bigger pie. The stars we see in the night sky are only those which are present in the Milky Way Galaxy.
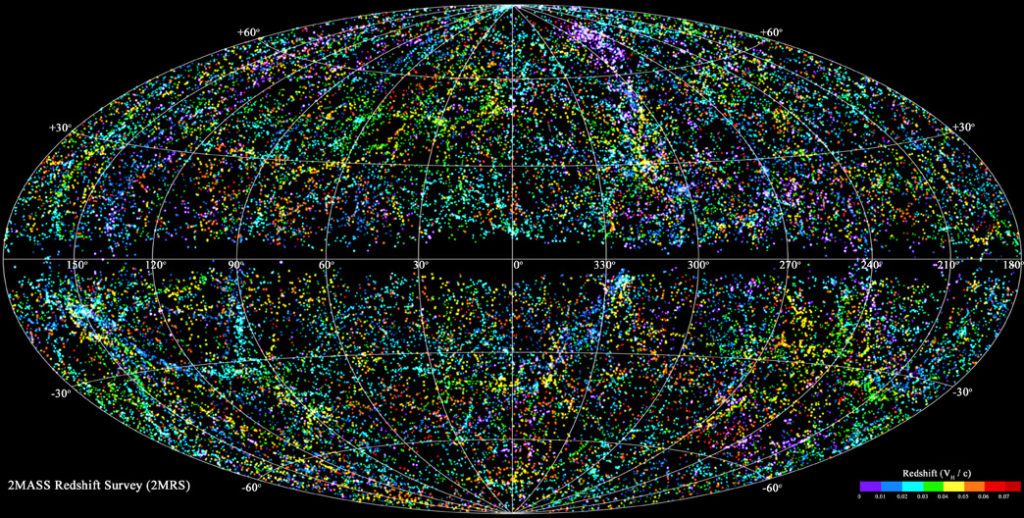
As we have already established, the observable Universe is much bigger than our wildest imaginations. It is only natural that researchers would want to quantify these cosmic distances as accurately as they can. The most recent effort, which started five years ago, has produced, as the researchers themselves call it “the largest three-dimensional map of the universe.”
The map, which is a product of the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), is a valiant effort to map the stars as accurately as we can. The SDSS is an international venture to map the expanding Universe and maybe help solve some of the pressing questions we have about it.
The map is truly impressive as it has mapped more than 2 million galaxies. The oldest ones that have been mapped are 11 Billion light-years away. The astronomers are hopeful that this new map will provide them with some valuable information to solve the mystery of “the gap.”
“The gap” is a mysterious period of the Universe’s expansion, which we do not know much about. Astronomers well understand the early expansion of the Universe as well as the recent expansion. However, there is an 11-Billion-year gap in between that the astronomers want to unravel.
The ancient expansion of the Universe is a very well-studied topic. This is thanks to the presence of the Cosmic microwave background radiation. It is the leftover radiation from the big bang, which is still hanging around the neighbourhood.
The recent expansion of the Universe is also well understood because of the observation tools at our disposal. We can measure how the distances between stars and galaxies change over time, to figure out how the Universe is expanding. The period in-between these two is a mystery. Light from far-away stars is too faint for any such observations.
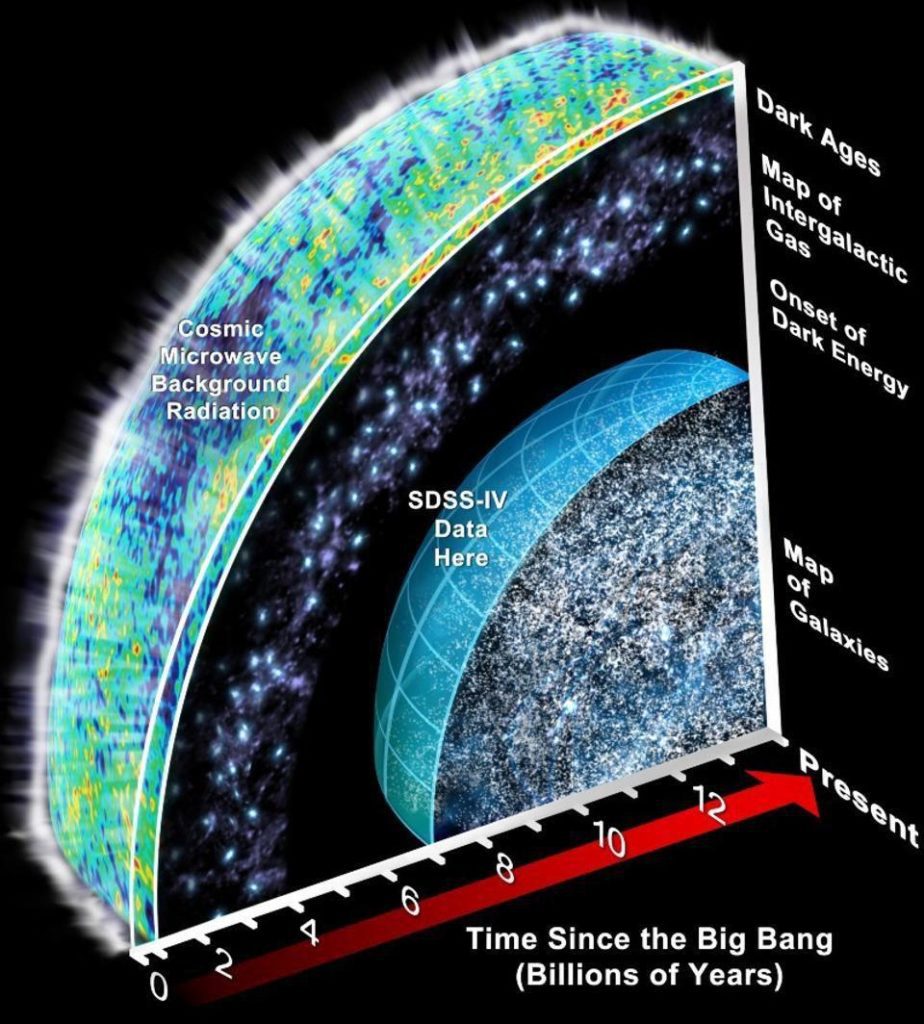
The new map might be able to help us fill that gap in our knowledge by providing some key insight into the position of the galaxies and the stars from that period. Hopefully, it will prove to be a great advantage in our quest to find out the true nature of our Universe.
Further Reading: