Quite surprising, isn’t it? Last night, Google announced the new Pixel 5 and Pixel 4a along with the Nest Audio and Google TV with Chromecast (which had leaked way before the release).
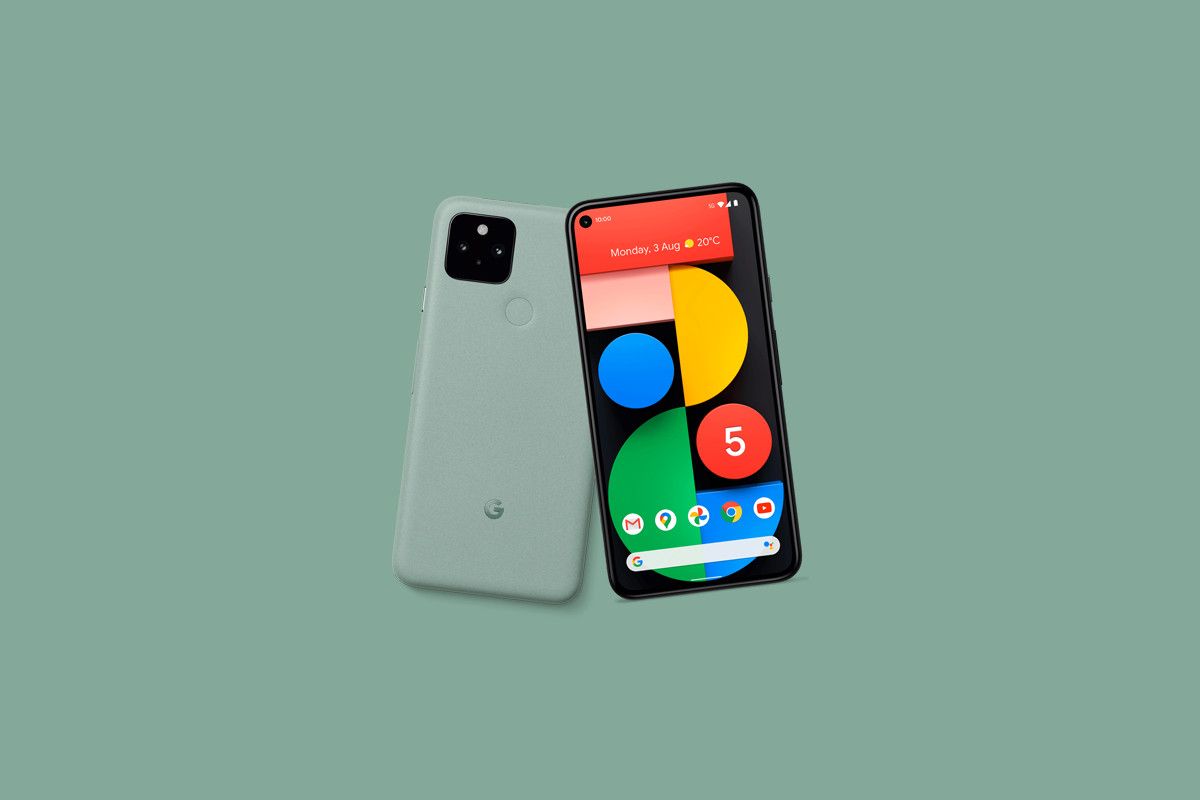

While launching the device, Google claimed that the Pixel 5 is made out the Aluminium body, and the device supports fast wireless charging (reverse wireless charging too!), which took the tech community by a storm. This is the first time we’re seeing a device which has a metal body and the phone supports wireless charging. How? Let’s take a look.
Also Read: Google launches the Pixel 5 at $699; Pixel 4a upgraded to 5G, Priced at $499
How Normal Wireless Charging Works
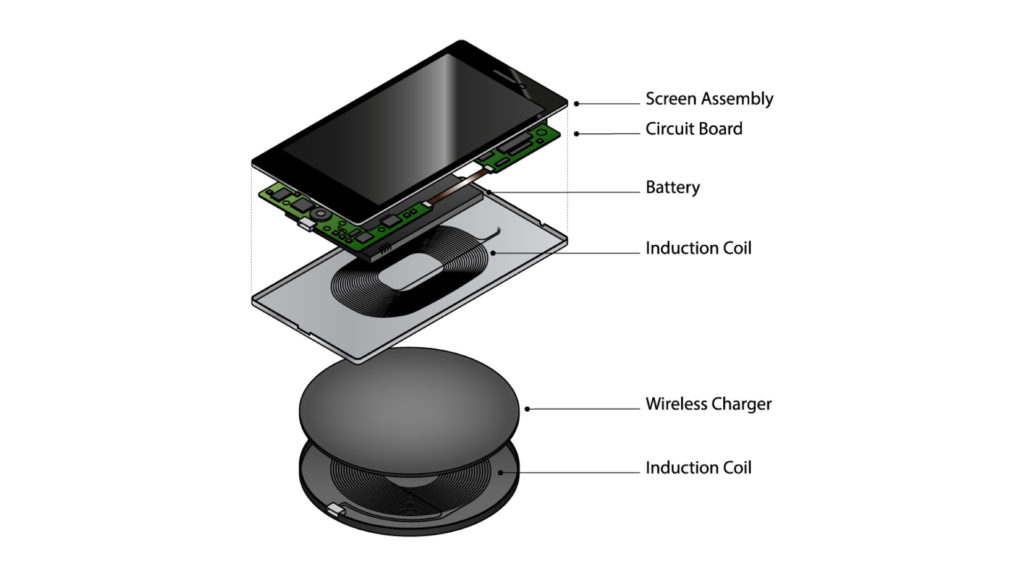
First, let’s understand how wireless charging works. There’s a simple technique in Physics (called Induction) behind this beautiful piece of tech. Wireless charging compatible phones have a coil inside the back (cover) of the phone, which is connected to the battery of the phone. The wireless charger also contains a coil to which the current is supplied when you plug-in the charger. When you put the phone on a wireless charger, due to induction, the current is generated in the coil (inside the charger) which in turn generates a current in the coil (inside of your smartphone) and power is supplied to the battery.
Up until now, smartphone manufacturers have had difficulties getting wireless charging to work with metal body smartphones. This is because the metal doesn’t let the electric field pass through it (called shielding effect) and hence smartphone OEMs have had to rely on glass or polycarbonate for the wireless charging to work.
Polycarbonate does work well with wireless charging, but smartphone manufacturers opt for a glass back, just to justify the price of a flagship, and give it a premium feel.
Pixel 5’s Wireless Charging

With the Pixel 5, Google has added an extra layer on top of the Aluminum build of the smartphone — called Bio-Resin — which another fancy name for super-thin plastic. This is the layer you’ll feel when you pick up a Google Pixel 5.
The metal behind the Bio-Resin layer is just to provide structural support to the phone. This ‘super-thin plastic layer’ allowed Google to put the wireless charging coil in the phone.
There’s a physical circular hole in the Pixel 5’s aluminium chassis, where the charging coil is, and Google says you shouldn’t be able to feel the coil since the bio-resin layer is apparently very sturdy, even with its thin design.
What do you think about this wireless charging solution. Will we see more metal body phones now? Let us know in the comment section below!

