Galaxies are beautiful to look at; they are a huge collection of solar systems and other cosmic entities that are held together by the sheer force of their collective gravity. This has made some photographs of these gargantuan objects the face of space science. It is not uncommon for people to imagine a galaxy whenever the word ‘space’ is mentioned to them.
These galaxies come in several shapes and sizes, and they are regulated by the invisible laws of Physics that determine what shapes these galaxies can take. For example, our Milky Way is shaped like a spiral, whereas there are other shapes as well.
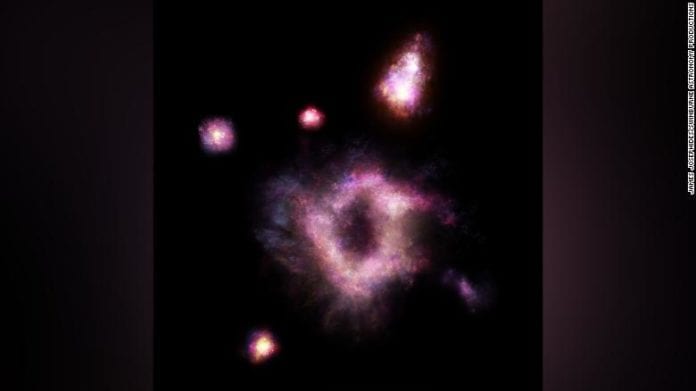
However, once in a while, astronomers discover some new things about these galaxies; most of the time, these are subtle things that cannot be visualized or observed directly. This is not true for the most recent discovery that a couple of Australian astronomers have made. A team of scientists have discovered one that looks like a ‘cosmic ring of fire’ in the early Universe. This doughnut-shaped galaxy could help the astronomers better understand how galactic structures form and evolve, especially since this galaxy was formed in the early Universe.

The mass of the newly discovered galaxy is almost the same as the Milky Way. However, one of the biggest distinctions is the giant gaping hole in the middle of this galactic structure. The image that was captured of the Galaxy shows us what it looked like about 11 billion years ago, which is just 3 billion years after the formation of the Universe itself.
The galaxy is of great interest to the researchers as they have never seen anything like it before. The galaxy has been named R5519 and is 11 billion light-years away from our Planet. The hole in the centre of the galaxy is about two billion times greater than the distance between Earth and the Sun.
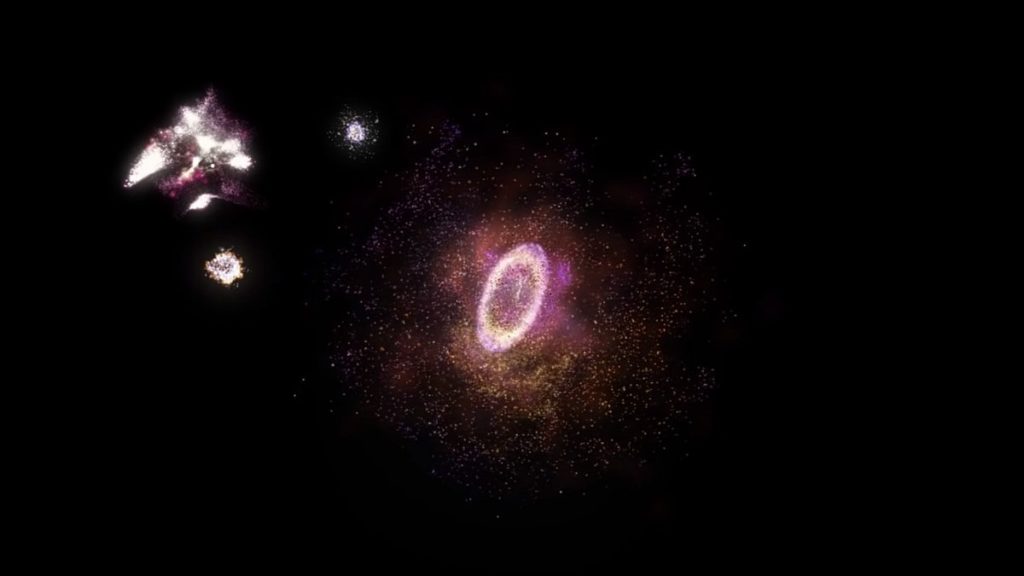

The rate of production of stars in R5519 is about 50 times higher than the Milky Way. The researchers utilized the spectroscopic data to identify and catalog it. It is the first galaxy that is a collisional ring galaxy in the early Universe. This means that it was formed by the collision of two galaxies back when the Universe was much younger. The careful study of this galaxy could help the researchers gain a better understanding of how our galaxy was formed.
Only time will tell what the researchers can learn from this cosmic ring of fire and how it translates into the current understanding of the laws of physics.
Further Reading: